2019/11/15 12:00 | Pageview:1657 | From: iotevolutionworld
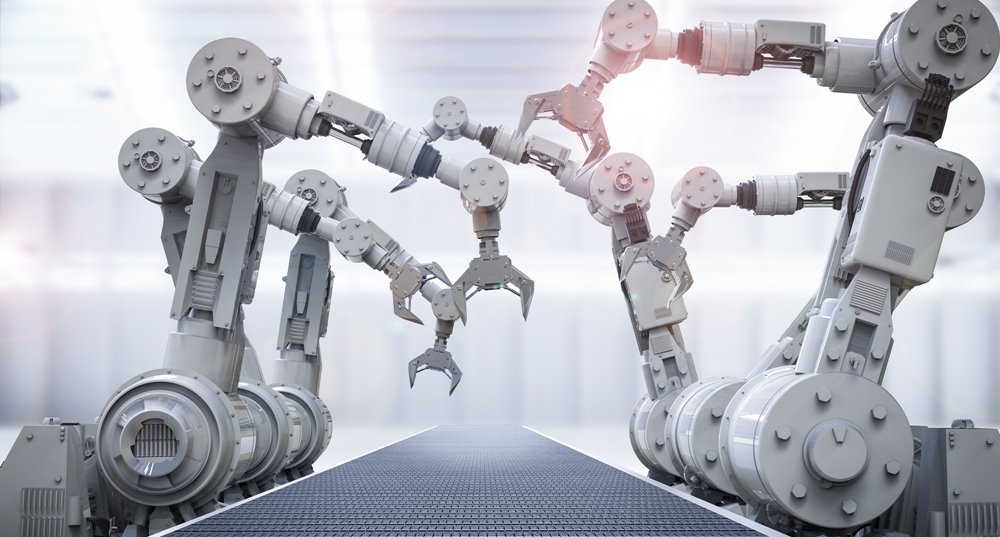

The manufacturing process includes advanced robotics at nearly every step. Investment in the technology reached $16.5 billion in 2018, a number that's expected to grow in the coming years.
Robots of today don't mimic designs from the past, which were immobile and built into one specific part of the manufacturing process. Instead, they seemingly have minds of own.
Cutting-edge robots, powered by advances in artificial intelligence and predictive analysis, make the manufacturing process safer and more efficient. Plus, manufacturers are using robots in entirely new ways.
AI and Collaborative Robotics
Artificial intelligence is changing how robots fit into manufacturing. AI-powered collaborative robots — sometimes called cobots — are designed to work alongside human workers, rather than replace them or act alone. Collaborative robots can fit just about any niche they need to in the manufacturing process. Still, most commonly used for quality assurance, transporting materials and providing real-time information to human workers.
These robots typically require little to no human supervision. In some cases, they can even use artificial intelligence-powered vision and image recognition to navigate factory floors by themselves. Therefore there's no need to rely on preset paths or human guidance.
Other AI innovations are making robot workers more cost-effective. Techniques like predictive maintenance, where AI finds patterns in preventative needs and determines when robots require repairs, are used to prevent serious damage or extended periods of downtime.
Harm and Risk Reduction
Robots can perform in dangerous environments and handle hazardous materials that would be harmful or fatal to human workers. Robots can also keep workers safe in situations where carcinogenic particles — like silica, metal or rock dust — are blasted into the local environment by the manufacturing process.
Techniques like automatic blasting — where robots are used in the cleaning, stripping or finishing of metal surfaces — can keep workers out of harm's way and prevent them from inhaling harmful dust and contaminants.
Robots can save employees from work that's repetitive or particularly hard on the body. While most people think of a single, serious event when they imagine a workplace injury, repetitive movements or postures can also cause severe damage to the body. Menial tasks, like bending over to pick up a delivered box, or turning a specific screw or component, can easily cause damage to joints, nerves and muscles. By performing these tasks for human workers, robots can save them from joint or tissue damage.
Robots can also save themselves in addition to human workers. These bots get outfitted with sensors that record and track important operational data. If a certain variable or set of factors cross the danger threshold — temperatures or pressures become too extreme, or dangerous chemicals reach high levels — the robot can immediately terminate the process and alert a supervisor. Human workers don't always have access to that kind of information, and may still be in danger after work stops.
These sensors won't always save a robot from damage or serious mechanical failure. Yet even in the worst-case scenario, a repair is less costly than the loss of human life.
24/7 Operations and "Lights-Out" Mode
The lights-out factory — one where human workers are unnecessary in the manufacturing process — is still many years from reality. Even in plants where most of the methods are automated, workers are necessary to complete the process.
Nevertheless, specific tasks or parts of the manufacturing process can be wholly automated. Some factories can continue to function even when no human workers are present. In one example, a manufacturing startup used a collaborative robot to assist human workers with the quality assurance process during the day. At night, the robot goes into lights-out mode, continuing to prepare parts until workers return the next morning.
The rise of the full lights-out factory won't be likely any time soon. Yet partial and overnight lights-out robotics are already making 24/7 operations possible. With collaborative robots, factories can be more efficient than ever. Robots can finish work even when employees aren't in the factory.
The Future of Robotics in Manufacturing
A new philosophy of robotics, along with advances in AI, predictive analysis and other technologies, is guiding robotic design. In modern factories, cobots work alongside workers instead of replacing them in the manufacturing process. As AI technology develops, these robots will become even more flexible and adaptable, able to complete tasks without the need for a human presence.
The future of robotics in manufacturing is collaborative — one where robots work alongside humans to improve efficiency and make processes safer. How robotics evolve as technology continues to advance?
 Loading...
Loading...